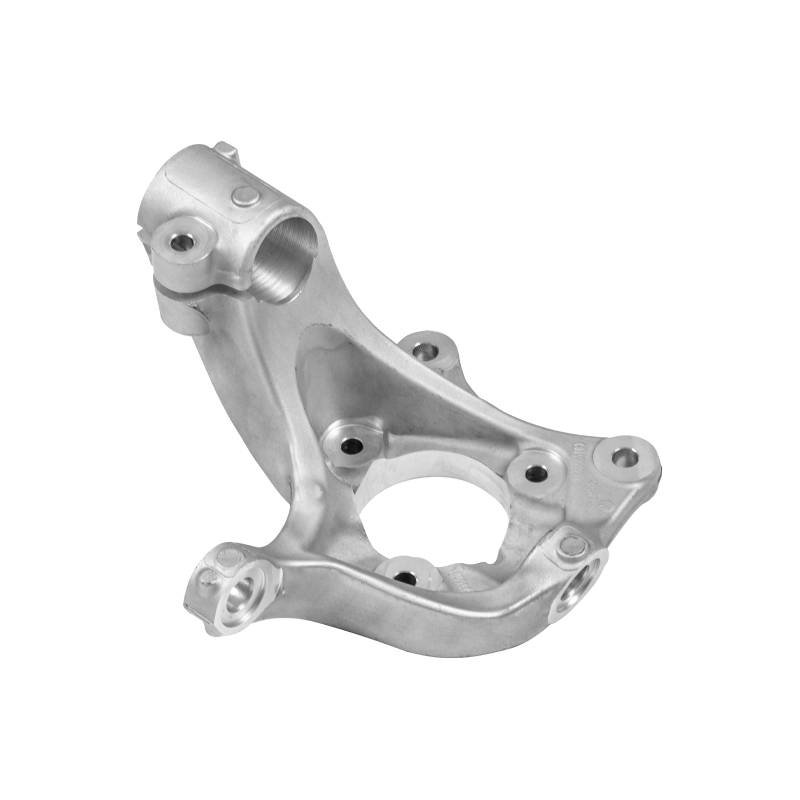
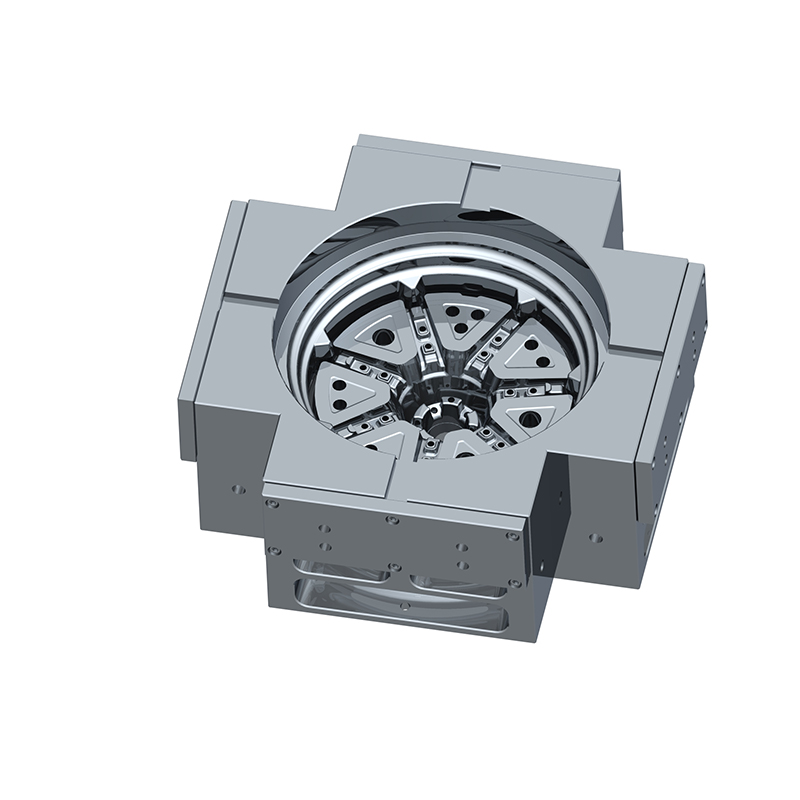
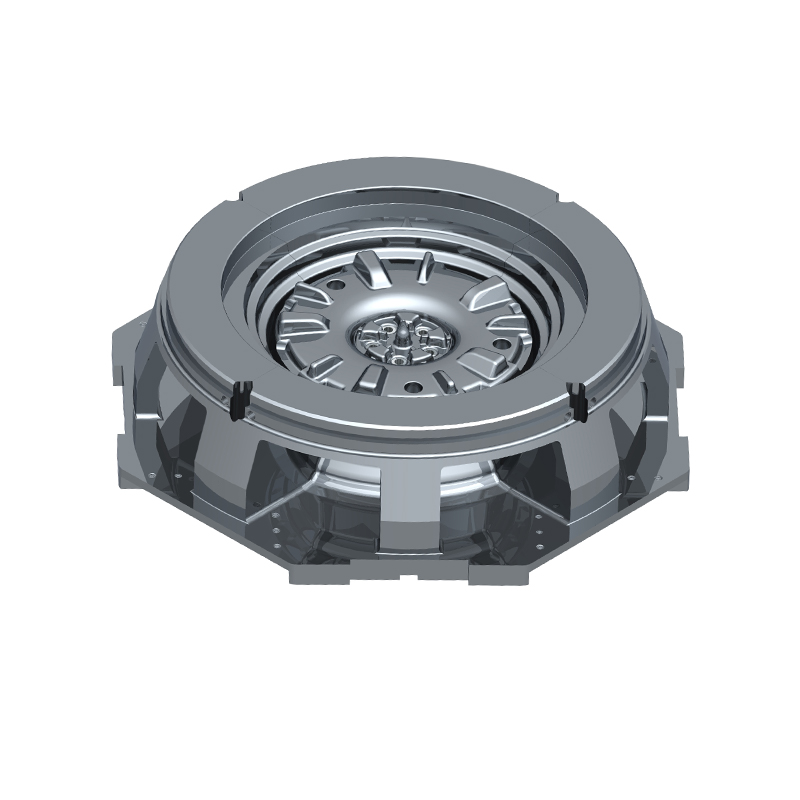
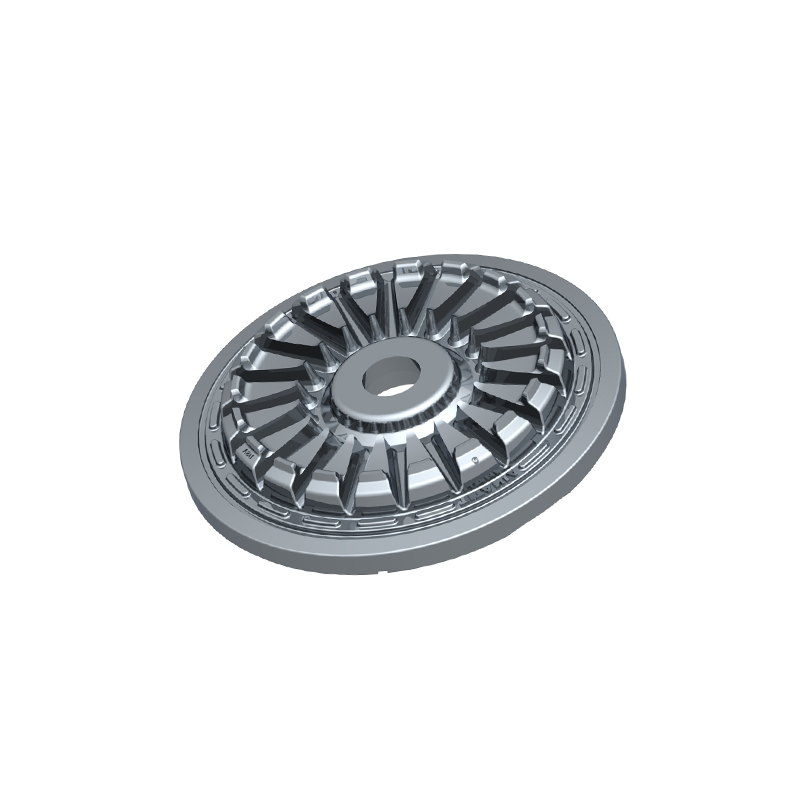
We offer molds for diverse industries, including automotive, military, and construction, enabling global competitiveness through innovation and expertise.
Custom Aluminum Alloy Casting Molds: What You Need to Know
1. Introduction: Why Custom Aluminum Casting Molds Matter
Custom aluminum alloy casting molds are a vital component in modern manufacturing, offering a high degree of flexibility and performance. Unlike off-the-shelf mold solutions, custom molds are specifically engineered to meet the dimensional and functional requirements of a unique part or product. This makes them ideal for industries that demand precision and high-performance materials, such as aerospace, automotive, consumer electronics, and medical devices. With the increasing demand for lightweight and corrosion-resistant materials, aluminum alloys have become a top choice for casting. Custom molds enable manufacturers to reduce waste, improve production efficiency, and ensure consistent product quality across production runs. This customization capability also supports prototyping and iterative design, helping companies reduce time to market while enhancing product innovation.
2. What Are Aluminum Alloy Casting Molds?
Aluminum alloy casting molds are specialized tools used to shape molten aluminum into desired forms. These molds are typically made from durable steel or other heat-resistant alloys to withstand the high temperatures of molten aluminum. The aluminum alloys used in casting often include silicon, magnesium, copper, or zinc to enhance mechanical properties such as strength, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance. There are various types of aluminum casting methods—die casting, sand casting, permanent mold casting, and investment casting—and each uses molds designed for specific applications. The key purpose of these molds is to provide accurate geometry, surface finish, and dimensional stability to the final product. A custom aluminum mold is tailored to produce parts with complex geometries, tight tolerances, and unique features that standard molds cannot achieve, making them indispensable for specialized manufacturing needs.
3. Advantages of Custom Molds vs. Standard Molds
Custom aluminum casting molds offer several advantages over standard, off-the-shelf molds. Firstly, they are designed with the specific geometry and functional requirements of a part in mind, resulting in better fit, finish, and performance. This customization minimizes the need for post-casting machining and finishing, reducing production time and cost. Secondly, custom molds can be optimized for faster cycle times and better heat dissipation, which improves throughput and extends mold life. Thirdly, they allow for enhanced design freedom, enabling the production of parts with intricate internal features, undercuts, and thin walls that may be impossible with generic molds. Finally, custom molds support branding and design differentiation, as manufacturers can integrate logos, text, or specific textures directly into the mold design. While custom molds may require a higher upfront investment, the long-term benefits in efficiency, quality, and flexibility often outweigh the initial cost.
4. Common Applications of Custom Aluminum Molds
Custom aluminum alloy casting molds are widely used across multiple industries due to their adaptability and performance. In the automotive industry, they are used to manufacture engine components, transmission cases, brackets, and lightweight structural parts. In aerospace, custom aluminum molds help produce aircraft interior components, housings, and precision brackets, where weight reduction is critical. The electronics sector uses aluminum molds to produce heat sinks, enclosures, and connectors that require excellent thermal conductivity and dimensional stability. In medical device manufacturing, aluminum molds are employed to create custom surgical tools, housings for diagnostic equipment, and ergonomic components. Consumer goods such as sporting equipment, kitchen appliances, and LED lighting fixtures are often produced using aluminum molds for their aesthetic finish and corrosion resistance. These molds enable companies to rapidly prototype, test, and launch new designs, making them essential for innovation-driven industries.
5. Key Factors in Designing a Custom Aluminum Casting Mold
Designing a custom aluminum casting mold requires careful consideration of several critical factors. The first is part geometry, which includes dimensions, complexity, and wall thickness. Complex shapes may require multi-part molds or specialized core inserts. Next is draft angle, which facilitates the removal of the part from the mold without causing damage. Adequate draft angles prevent sticking and reduce wear on the mold. Cooling channels must be strategically placed to manage heat dissipation and reduce cycle times. Gating and venting systems are essential for controlling the flow of molten metal and eliminating air pockets, which can cause defects. Material shrinkage also needs to be accounted for in the mold dimensions to ensure accurate part size after cooling. Finally, the surface finish and tolerances must align with the end-use requirements of the part, especially if the product will undergo minimal post-processing. Collaborating with experienced mold designers and foundries is key to ensuring that all these factors are optimized.
6. Material Considerations: Choosing the Right Aluminum Alloy
Not all aluminum alloys are created equal, and selecting the right one for your custom casting mold is essential for achieving the desired mechanical and thermal properties. Common aluminum casting alloys include A356, 319, 535, and 713, each offering different balances of strength, corrosion resistance, machinability, and thermal conductivity. For example, A356 is widely used due to its excellent castability and good mechanical properties, making it suitable for aerospace and automotive parts. 319 is favored for its high corrosion resistance and is often used in marine applications. 535 offers exceptional strength and is ideal for structural components, while 713 has excellent wear resistance for high-load applications. The choice of alloy also affects mold design, particularly in terms of cooling requirements, shrinkage behavior, and tool wear. Additionally, environmental factors, such as exposure to saltwater, chemicals, or extreme temperatures, must be considered when choosing an alloy. Consulting with a metallurgical expert can help determine the best alloy for your specific application.
7. Manufacturing Techniques: CNC Machining, Die Casting, and More
Custom aluminum molds are manufactured using a variety of techniques, each suited to specific requirements for precision, volume, and cost. CNC machining is commonly used for creating mold cavities and cores with high precision. It allows for tight tolerances, complex geometries, and rapid prototyping. Die casting involves injecting molten aluminum into a steel mold under high pressure. This method is ideal for high-volume production and yields parts with excellent surface finishes and dimensional accuracy. Sand casting uses sand-based molds and is suitable for lower-volume production or larger components that don’t require fine details. Permanent mold casting is similar to die casting but operates at lower pressures and is often used for thicker, more robust parts. Additive manufacturing (3D printing) is also emerging as a tool for creating mold inserts or prototypes quickly. Each method has trade-offs in terms of cost, cycle time, and achievable part features, so choosing the right one depends on the project’s goals, complexity, and budget.
8. Cost Factors and Lead Time for Custom Mold Production
The cost of producing a custom aluminum casting mold varies significantly depending on the complexity of the design, the size of the mold, the alloy used, and the required precision. Initial costs include mold design, prototyping, tooling, and testing. For high-precision molds, CNC machining and surface treatments (like polishing or coating) can drive up costs. These upfront investments often pay off over long production runs due to lower per-part costs and reduced defects. Lead time is another critical factor, typically ranging from 2 to 12 weeks depending on the mold complexity and manufacturer workload. Rush orders can increase both cost and risk. It’s important to consider total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes not only mold fabrication but also maintenance, lifespan, and part yield. Budget-conscious companies should work with mold manufacturers who offer transparent quotes, design-for-manufacturing (DFM) consultations, and scalability options to ensure cost-effectiveness and long-term value.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体