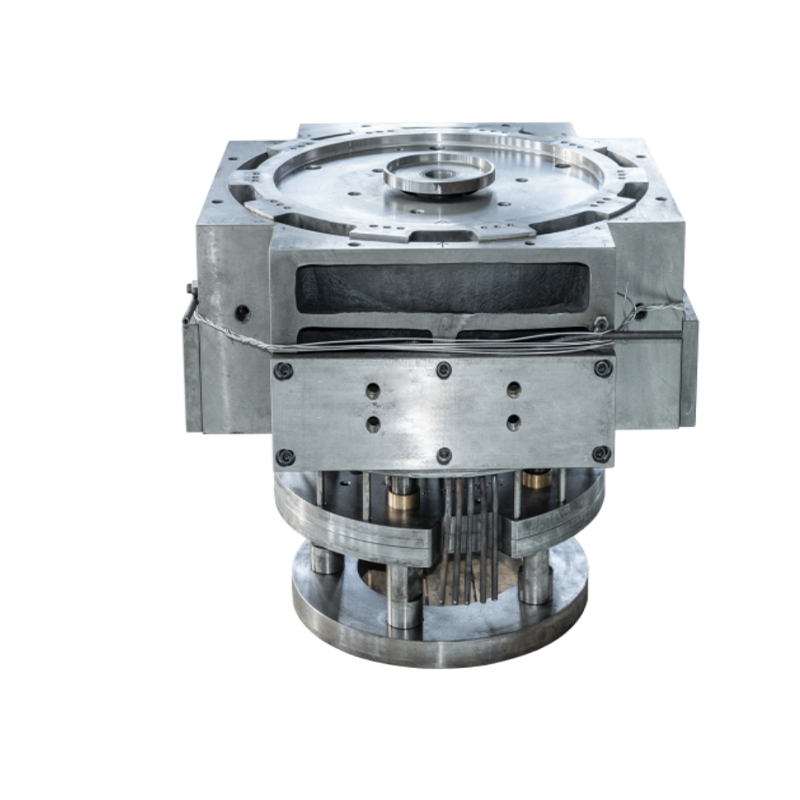
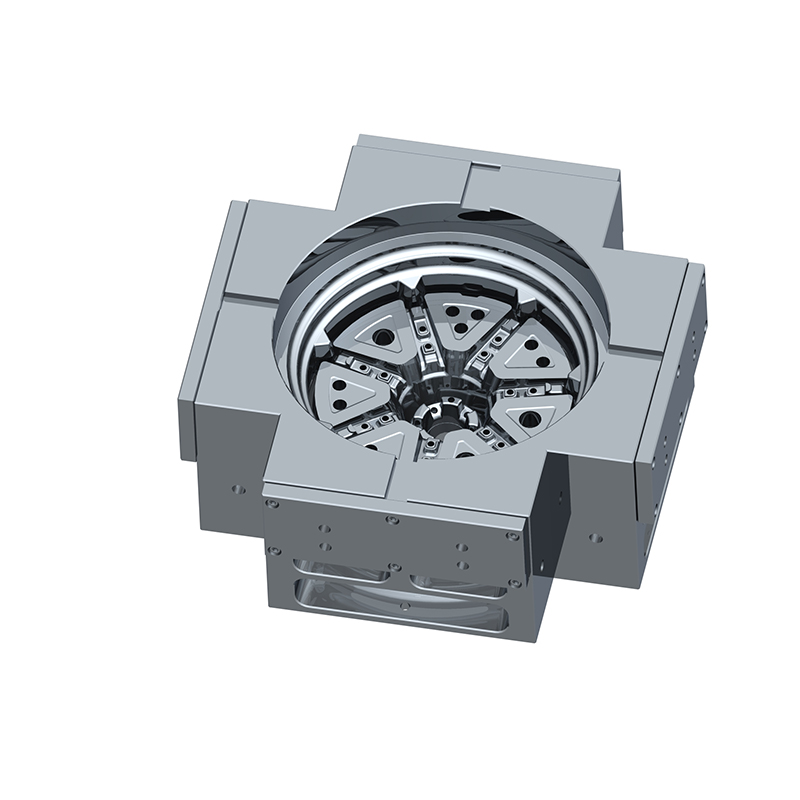
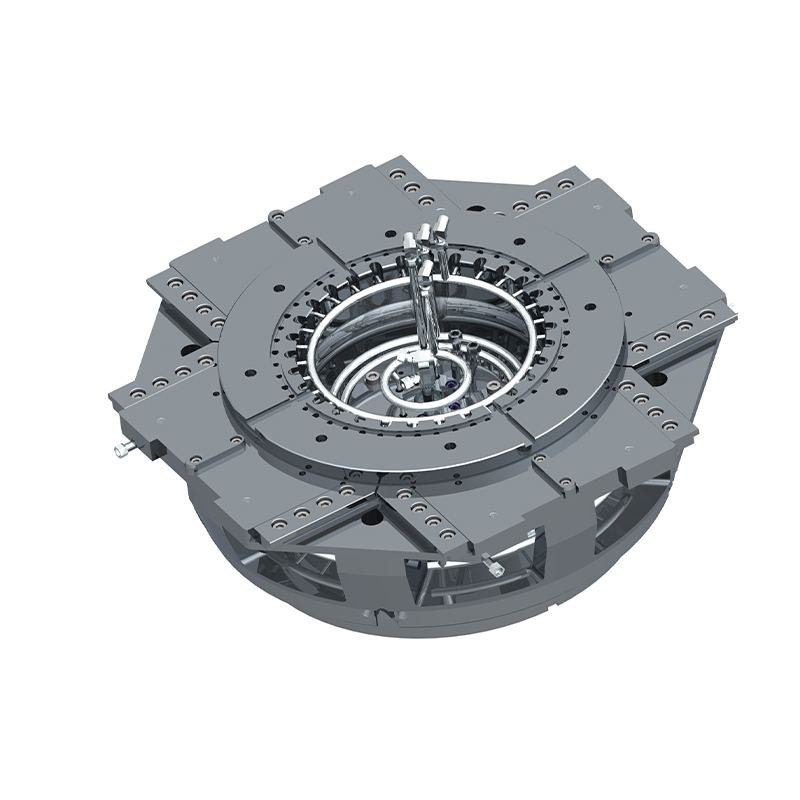
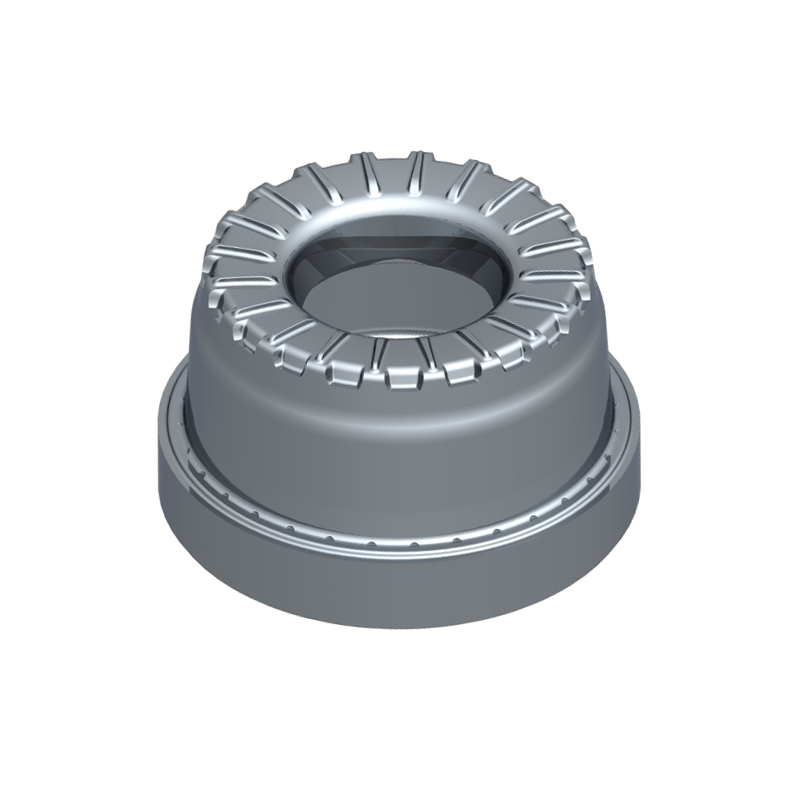
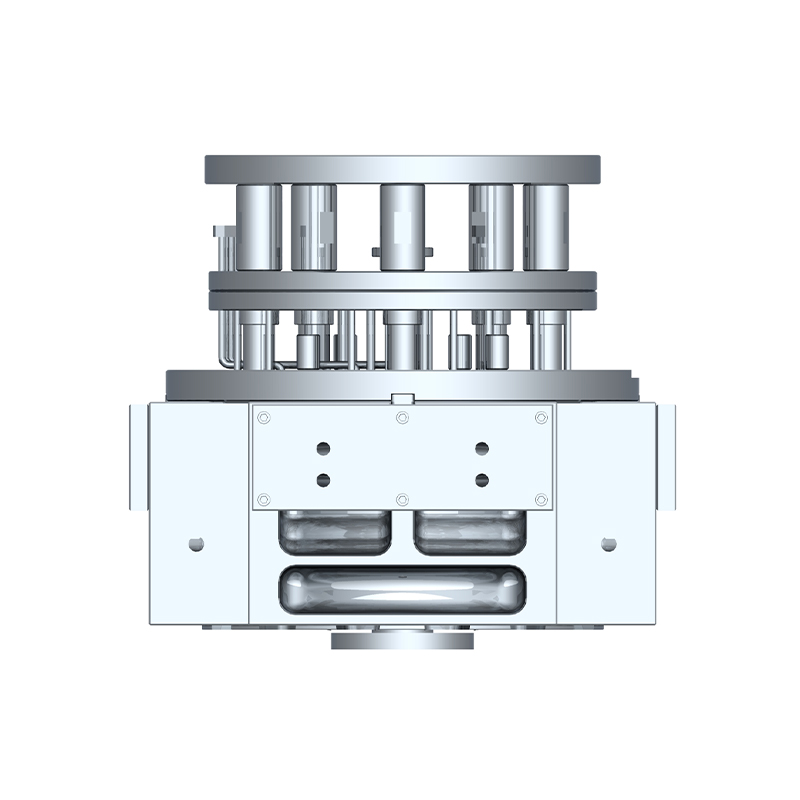
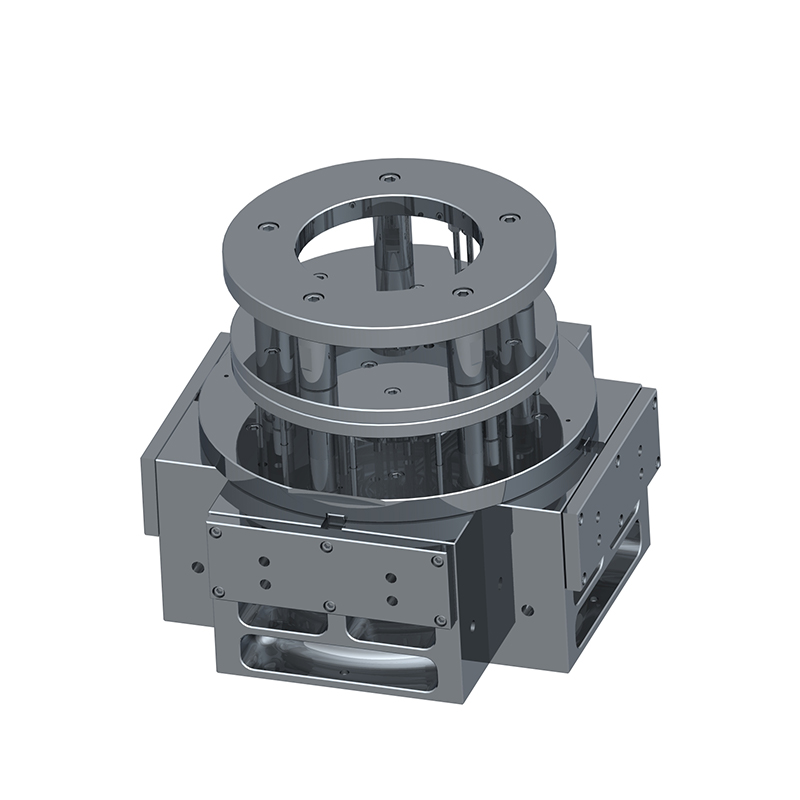
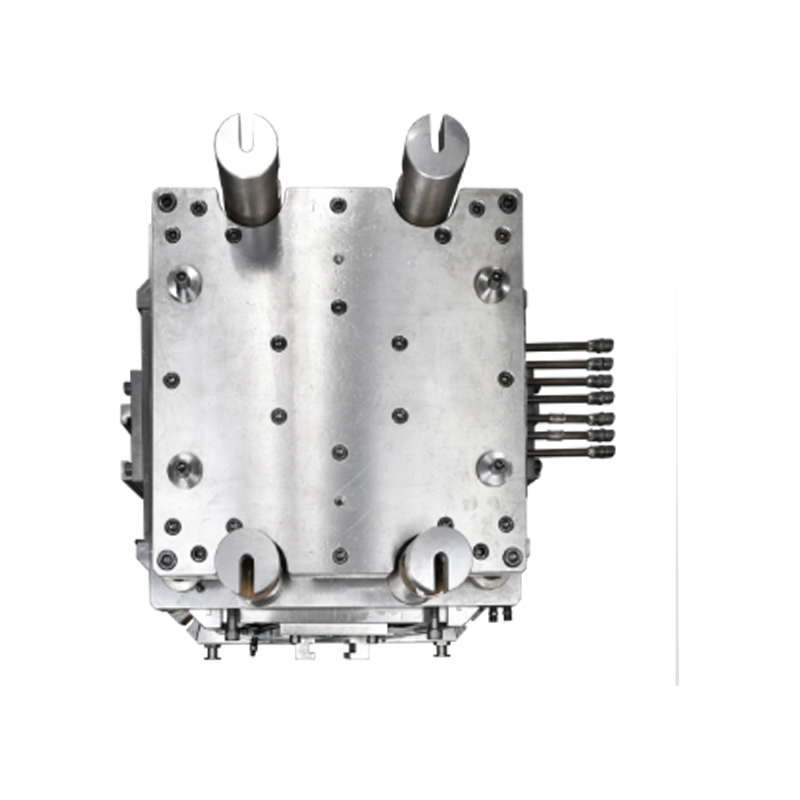
We offer molds for diverse industries, including automotive, military, and construction, enabling global competitiveness through innovation and expertise.
Casting Tooling Fixtures vs. Conventional Molds: A Comprehensive Comparison for Engineers
In modern manufacturing, casting tools and molds are crucial for ensuring the production of high-precision parts. Whether in the automotive, aerospace, or electronics industries, precise and efficient production processes rely on the right tools. For engineers, understanding the difference between Casting Tooling Fixtures and Conventional Molds is essential for making the right production decisions.
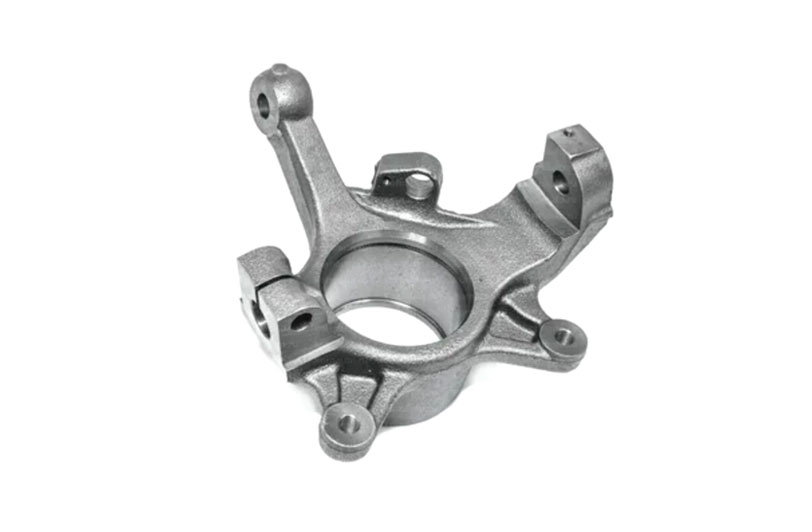

What Are Casting Tooling Fixtures?
Casting Tooling Fixture Molds are specialized tools used to support molds during the casting process. Their primary function is to ensure that the castings remain in the correct position throughout production. By securely holding the part or mold in place, casting tooling fixtures minimize deformation and errors, which enhances production accuracy. These fixtures are usually made from high-strength metals or alloys, offering properties like high-temperature resistance and corrosion resistance to perform well in harsh environments.
Features:
- High-precision support: Casting tooling fixtures ensure the accurate positioning of parts during production, reducing dimensional errors.
- High-temperature resistance: Fixtures are exposed to high temperatures during casting, so they need to have strong heat resistance.
- Adaptability to complex shapes: Unlike conventional molds, casting tooling fixtures can accommodate parts with more complex shapes.
- Increased production consistency: By minimizing errors during casting, tooling fixtures significantly improve product consistency.
What Are Conventional Molds?
Conventional Molds refer to the standard molds used in the casting process, typically for simple or standardized parts. Conventional molds are usually made of steel, aluminum, or other alloys and are designed to withstand prolonged use at high temperatures. Their main function is to shape molten metal into the desired casting by cooling and solidifying it within a defined cavity.
Features:
- Suitable for standardized parts: Conventional molds are ideal for mass-producing parts that follow a consistent design, particularly in large-scale production.
- Simple structure: The design of conventional molds is generally simple and works well for most common casting requirements.
- Long service life: Due to optimized design, conventional molds tend to last longer during the casting process.
- Lower cost: Conventional molds are typically more affordable, especially for large-volume production runs.
Key Differences Between Casting Tooling Fixtures and Conventional Molds
Understanding the key differences between Casting Tooling Fixtures and Conventional Molds is crucial when selecting the appropriate casting tool. Below is a comparison of both in several key dimensions.
Design Flexibility
- Casting Tooling Fixtures: Casting tooling fixtures are highly customizable and can be designed to accommodate complex-shaped parts. This makes them highly flexible and suitable for parts with intricate geometries.
- Conventional Molds: Conventional molds are typically more rigid in design and are best suited for parts with simple, standardized shapes. They are less adaptable for complex or custom parts.
Production Speed
- Casting Tooling Fixtures: Casting tooling fixtures are typically used in low-to-medium volume production. While they may require more setup time and adjustments, once in place, they can produce highly accurate results.
- Conventional Molds: Conventional molds are more suited for high-volume production since their setup and use are quicker. They excel in mass production scenarios where speed is critical.
Cost
- Casting Tooling Fixtures: Due to the need for customization and precise engineering, casting tooling fixtures tend to have a higher initial cost. However, they are more suitable for small-batch and high-precision production.
- Conventional Molds: Conventional molds are generally less expensive to manufacture, especially when used for high-volume production runs. They offer cost savings in large-scale production.
Precision and Accuracy
- Casting Tooling Fixtures: Casting tooling fixtures provide higher precision during production, reducing errors in the casting process. This makes them ideal for producing parts with high tolerances and complex designs.
- Conventional Molds: While conventional molds provide some level of precision, they may not meet the high-precision requirements for complex or intricate parts. They are often less accurate than tooling fixtures.
Material Compatibility
- Casting Tooling Fixtures: Fixtures are versatile and can work with a wide range of materials, including high-temperature alloys and specialized metals.
- Conventional Molds: Conventional molds are best suited for standard materials such as aluminum, steel, or copper, making them less adaptable to more complex or high-temperature casting requirements.
Comparison Table: Casting Tooling Fixtures vs. Conventional Molds
| Feature | Casting Tooling Fixtures | Conventional Molds |
|---|---|---|
| Design Flexibility | Highly flexible, customizable for complex shapes | Limited flexibility, suited for standard parts |
| Production Speed | Lower speed, ideal for low-to-medium volume | Faster production, suitable for mass production |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, suitable for precision work | Lower cost, cost-effective for high-volume production |
| Precision and Accuracy | Higher precision and consistency | Moderate precision, may require additional adjustments |
| Material Compatibility | Works with a wide range of materials, including high-temp alloys | Best for standard materials like aluminum, steel |
When to Use Casting Tooling Fixtures vs. Conventional Molds?
When to Choose Casting Tooling Fixtures?
- High Precision Requirements: If you need highly accurate parts, especially those with complex geometries, casting tooling fixtures are the best choice. They ensure proper alignment during the casting process, minimizing deviations.
- Small to Medium Batch Production: For small-batch or high-precision production, casting tooling fixtures offer the required accuracy and consistency.
- Complex Part Designs: If the part design is intricate or requires specialized support structures, casting tooling fixtures offer the flexibility needed for custom solutions.
When to Choose Conventional Molds?
- High Volume Production: Conventional molds are ideal for fast, high-volume production. Their quick setup and efficient use make them perfect for mass production of standardized parts.
- Cost-sensitive Applications: If the budget is tight, particularly in large-volume production, conventional molds offer significant cost savings.
- Standard Parts: For parts with simple shapes and lower precision requirements, conventional molds can meet production needs without unnecessary complexity.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体